
St. Petersburg Branch of S.N. Fyodorov "Eye Microsurgery" started out a new direction - consultations, diagnostics and medical assistance concerning reconstructive and plastic ophthalmic surgery, and ophthalmic oncology with organ-preserving principle.
It is the first time we started to perform the most complicated operations using endovitreal micro surgery, transscleral and endolaser thermotherapy in case of intraocular neoplasms (director of St. Petersburg Branch Doctor of Medicine, Professor, Honored doctor of Russian Federation Boiko Ernest Vitalyevich as a surgeon). Direction is supervised by Deputy Director for Scientific and Research Work Doctor of Medicine, Professor, Honored doctor of Russian Federation Panova Irina Evgenyevna, a well-known specialist in the field of ophthalmic oncology.
For a preliminary correspondence consultation on the question of the feasibility of a diagnostic examination, consultation and subsequent hospitalization at St. Petersburg Branch patient should send the following information to our email address cmc@mntk.spb.ru:
All documentation sent by e-mail will be replied within 15 working days.
*- not more than 1 month old
Personal consultations are carried out by Deputy Director for Scientific and Research Work, Doctor of Medicine, Professor, Honored doctor of Russian Federation Panova Irina Evgenyevna according to the schedule by appointment on Mondays 14.00-17.00. Appointment on consultation within CHI (compulsory health insurance) is made by information and reference unit of the Branch, fee-based consultations by phone 8 (812) 324-66-66 on work days 9.00 -17.00.
To make an appointment You need to present:
(if one of these is missing, then consultation can be fee-based only)
* - not more than 1 month old
Among all malignant ocular neoplasms eyelid skin tumors are most common. These can be pigmented tumors (melanoma) and non-pigmented (cancers) arising from epidermis and eyelid glands.
Pathology can occur on the background of various pre-cancerous diseases: cutaneous horn, senile keratosis, xeroderma pigmentosum, papilloma, as well as on the background of scars after burns. Melanoma more often develops from benign pigmented neoplasms (melanosis, nevi).
Risk factors for these diseases are solar insolation, heredity, ionizing radiation, chemical exposure.
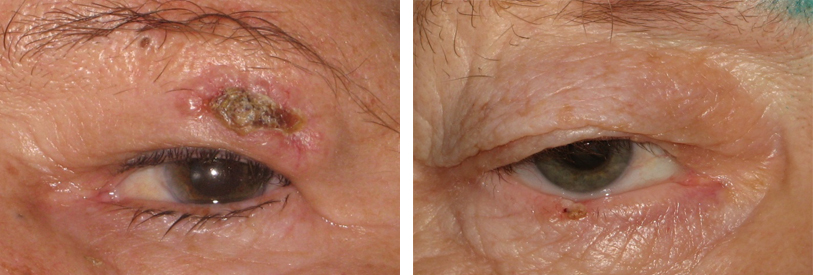
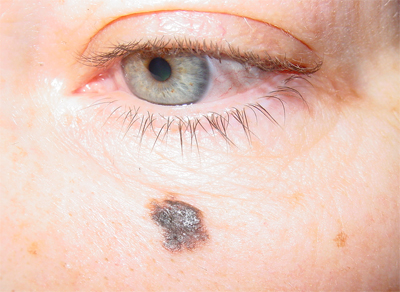
Additional symptoms include absence of the skin pattern, peeling, appearance of redensifications on the pigment tumor surface, increase of the lymph nodes closest to the tumor.
Great importance for early diagnostics of melanoma and eyelid skin cancer is a self-diagnostics and regular examinations by ophthalmologist. Do not try to cure yourself! When eyelid neoplasms appear, you should consult an ophthalmic oncologist, who, after a visual inspection and additional examinations will confirm or exclude the tumor-like nature of eyelid skin neoplasm.
Surgical treatment is the main for eyelid skin tumors. In St. Petersburg Branch we successfully perform microsurgical tumors removal using radio wave surgery (radio knife), and one-step with reconstructive and restorative stage.
During operation of the microscope allows you to evaluate the necessary boundaries of the excision of the tumor, which provides confidence in the complete removal of the tumor. Radiosurgery determines the minimal damage to the surrounding tissues and the best scarring, and the use of a wide variety of plastics results in a satisfactory functional and cosmetic result.
Intraocular melanoma is a malignant tumor that can appear in different parts of the vascular tract of the eye - iris, ciliary body and choroid. It develops due to malignant transformation of melanin pigment-forming cells. It is characterized by infiltrative growth, lymphogematogenous metastasis. Disease prevails in women, its peak occurs at the age of 55-60 years.
Uveal melanoma origin is still unknown, however, there are some factors that can affect the occurrence of the disease:
Tumor belongs to the "hidden" locations and beginning of the disease may be asymptomatic. For early detection of iris melanoma it is very important to detect appearance or pigment spot growth on the iris, any changes in the shape of the pupil.
Ciliary body melanoma is asymptomatic. It is possible to make the diagnosis at early stages if there is a careful examination with maximum dilation of the pupil.
Choroid melanoma. Depending on localization (central, equatorial-peripheral) complaints will be about visual acuity decrease, “spots”, “sparks”, “veils” in the field of view, pain.
Progression leads to complications development such as retinal detachment, cataract, glaucoma, tumor germination beyond the eyeball with the development of exophthalmos, possible destruction of the walls of the orbit, germination in the surrounding structures (in the brain, paranasal sinuses). Generalization of the process is accompanied by the appearance of hematogenous metastases, most often metastases are detected in the liver (93%), lungs (24%), metastases to the lymph nodes, bones, brain, skin, subcutaneous tissue, spleen, other eye and orbit are less commonly diagnosed.
Systematic examination. Fundus examination with dilated pupil.
Diagnosis is usually made on the basis of specific signs. Ophthalmoscopy and biomicroscopy are the main diagnostic procedures. They are harmless and painless. Ultrasound examination of the eye is used as additional method according to indications, as well as optical coherent tomography, dye angiography, MRI or computed tomography. In exceptional cases, an aspiration biopsy from a tumor tissue is performed.
Treatment can be with organ preserved and with organ liquidation. Choice depends on disease stage. At early stages (1-2 stage) it is possible to perform organ-preserved treatment – brachytherapy (exposure of tumor to radiation using special radioactive sources), thermotherapy, and surgical methods - endoresections, one block tumor removal. Among liquidation methods should be mentioned eyeball enucleation and orbit evisceration. Introduction of plastic stump surgery using biomaterial after enucleation allows to get the best cosmetic effect while performing an individual eye prosthetics.
Today almost every possible treatment method is widely used in St. Petersburg Branch of S. Fyodorov “Eye microsurgery”.
Patients with intraocular melanoma are subjected to life-term supervision and regular check-ups once every three months approximately during the first year after treatment, once every 6 months during the next year with obligatory ultrasound orbits examination every checkup. Once a year CT/MRT of orbits is performed once a year if necessary. Overall clinical and instrumental examination of the patient is required to exclude the generalization of the process, with consultation by oncologist, at least once a year.
Due to modern medicine achievements the possibility of full recovery in case of uveal melanoma is quite big if it was found at its earliest stages.
Malignant conjunctival tumors usually occur as conjunctival cancer or melanoma developed primarily or together with benign tumors and precancerous diseases.
Tumors occur at the age of 40-60 and are characterized by extremely aggressive development course, quick growth, growth into the eyeball, through the orbit and surrounding tissues, and gives metastatic spreading to regional lymphatic glands.
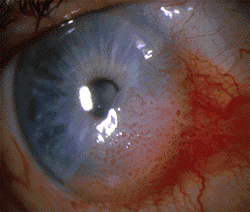
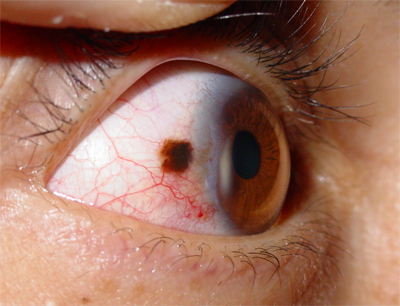
Self-diagnostics and regular follow-up examinations by ophthalmologist have a great importance for early diagnostics of conjunctival tumors. You should not medicate yourself! When conjunctival neoplasms appear, you should consult an ophthalmic oncologist, who on the basis of a visual inspection and additional examinations, will confirm or exclude the tumor-like nature of the neoplasm.
Surgical method is the main treatment method for malignant tumors. Removal of tumors using radio wave surgery (a radio wave knife) is successfully used in St. Petersburg Branch of S. Fyodorov “Eye microsurgery” simultaneously with reconstructive and plastic stage.
Using microscope during operation helps to estimate the dissection borders for tumor and to be sure that it is fully removed. Radio surgery determines the minimum damage of surrounding tissues and formation of a delicate scar. Tissues volume recovery which were removed from the eyeball surface is a very important moment and for this purpose can be used patient’s own tissues or alloplants.
Determination of the tumor histological affiliation is an important advantage of surgical treatment, which allows to choose the further treatment tactics and determine the necessity for additional radiation or chemotherapy.
Cryogenic exposure is one of the less commonly used methods, which is justified in case of benign eyelid skin tumors.
The disease prognosis depends on the time when tumor was found, on stage of the process and its histological affiliation.
Orbit is a space behind the eye, separated by the bone walls of paranasal sinus and brain, filled with adipose tissue, blood vessels, nerves, eyeball.
Orbital tissues variety makes a wide range of tumors, of which benign hemangiomas are the most popular, and more seldom are malignant tumors – sarcomas, lymphomas, cancers. Recently malignant tumors have a tendency of “rejuvenation” – up to 25% of them occur at the age of under 20.
Main symptoms of a starting tumor are bulging of the eyeball (exophthalmos), doubling (diplopy), droopy eyelid (ptosis), limitation of motion, moderate pain. Mainly it is a one-sided process.
Apart from overall ophthalmic examination the most important thing for diagnostics is performance of additional examinations like ultrasound study of orbits, computer (CT) or magnetic resonance tomography (MRT), choosing the method of diagnostic examination is up to a specialist.
The main method of treatment is orbitotomy - to remove the tumor surgically.
Treatment is planned considering individual anatomical and topographic features of the orbit, size of the tumor, its type, its prevalence, state of bone walls and regional lymph nodes, and presence of distant metastases. Conservative organ preserving treatment is preferred. Wait-and-see strategy is not allowed!
In St. Petersburg Branch of S. Fyodorov "Eye Microsurgery" all possible surgery is used during this operation. In some cases, biopsy of the tumor may be required to check its histological affiliation and determine further treatment tactics (in particularly, if there is a need for radiation or chemotherapeutic stage).
The prognosis depends on the type of tumor, time when it was found and on the extent of treatment.
Примите, пожалуйста, участие в опросе о качестве нашего сайта